
- Home
-
Services
 Leading molecular discovery services
Leading molecular discovery services
 Antibody Discover Service
Antibody Discover Service
 Technology platform
Technology platform
 Technology optimization service
Technology optimization service
- Products
- Resources
- Publication
- Contact Us

 Leading molecular discovery services
Leading molecular discovery services Antibody Discover Service
Antibody Discover Service Technology platform
Technology platform Technology optimization service
Technology optimization service
Membrane Protein Expression in VLPs
Virus-like particles (VLPs) are multi-subunit, self-assembling protein structures that are consistent or highly correlated with the overall structure of their natural virus counterparts, and many studies have demonstrated that VLPs have high immune response stimulating activity compared to other subunit vaccines.The highly repetitive amino acid (AA) template displayed on the surface of VLPs induces B-cell activation and high titers of antibody production.VLPs can be classified into two major categories: capsid-free VLPs and capsid-enriched VLPs.
VLPs can be divided into two main categories: non-encapsulated VLPs, which can be subdivided into single-coated VLPs (e.g., those derived from caliciviruses, papillomaviruses, and microviruses) and multi-encapsulated VLPs (e.g., those derived from infectious bursa viruses, polioviruses, and echoviruses). Vesicular VLPs usually consist of matrix proteins encapsulated in lipid membranes originating from the expression host for the expression of multiple transmembrane proteins, such as Claudin 18.2, GPRC5D, STEP1, Napi2b, and others.
NBbiolab has established a VLP (virus-like particle) technology platform based on the HEK293F expression system, and can provide customized vesicle-free VLP and vesicular VLP protein services, which are able to display the target proteins intact on the surface of the VLP and enhance the immune response. For vesicle-free VLP, Apak Bio also provides scaffolds based on Ferritin, MS2, mi3 & I53-50, etc., which is very convenient for customers to assemble VLP by themselves.
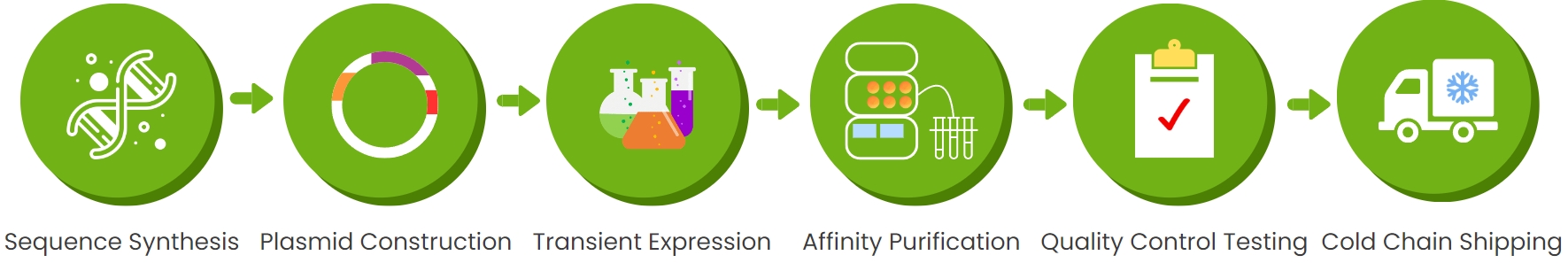
Service Process
Service Advantages


Tel:+86 4008677715
E-mail:service@nb-biolab.com
Address:SME Incubation Park, 319 Qingpi Avenue, Chengdu, China.
Working time:9:00-18:00