
- Home
-
Services
 Leading molecular discovery services
Leading molecular discovery services
 Antibody Discover Service
Antibody Discover Service
 Technology platform
Technology platform
 Technology optimization service
Technology optimization service
- Products
- Resources
- Publication
- Contact Us

 Leading molecular discovery services
Leading molecular discovery services Antibody Discover Service
Antibody Discover Service Technology platform
Technology platform Technology optimization service
Technology optimization service
Phage Display Platform
Principle of Phage Display Technology
Phage display screening is a well-established technique that identifies antibody fragments and other binding molecules against desired targets. The method involves the expression of foreign proteins as fusions to the coat protein III of a bacteriophage M13. The libraries of phage-displayed peptides or proteins are physically linked to their encoding nucleic acid, facilitating the selection of binding partners for various target types through iterative rounds of in vitro panning and amplification, followed by DNA sequencing.
Phage Display Library construction
Our platform ensures exceptional library quality through rigorous validation processes:
1. Primer Optimization: We use proprietary primers designed to comprehensively cover all HcAb germline sequences.
2. Zero-Background Cloning: By employing background-free cloning technology, we guarantee 100% VHH insertion efficiency.
3. Library Capacity: We guarantee a library size of over 1×10^9 CFUs.
4. Clonal Uniqueness: After randomly selecting 48 clones for Sanger sequencing, we ensure 100% clonal uniqueness with no sequence duplication detected.
5. Sequencing Depth Analysis: We guarantee an >90% correctness rate for ORFs following sequencing of the 48 selected clones.
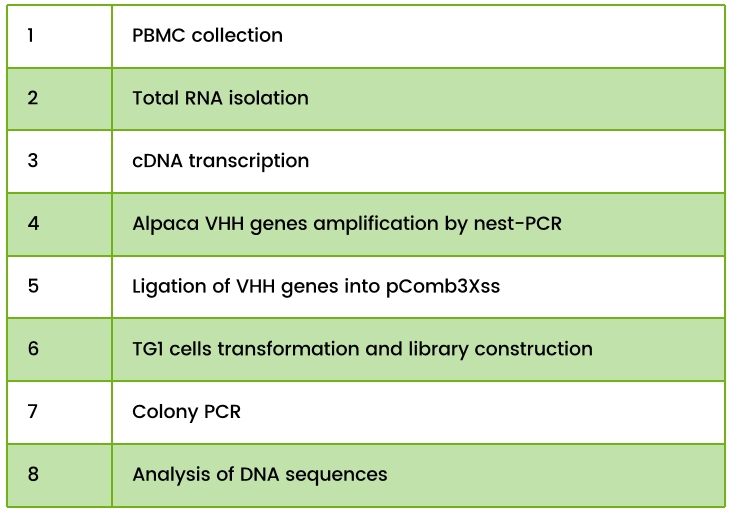
Table 1. Phage Display Library Construction Workflow Steps
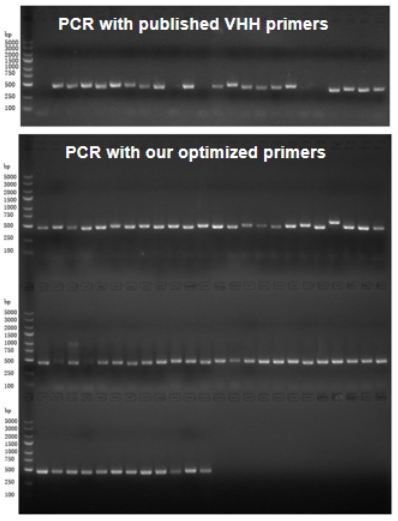
VHH Primer Optimization
Published VHH primers have limited germline sequence coverage. Our optimized primers effectively increase PCR amplification yield and enhance the diversity of VHH clones.
Phage Display Screening Procedures
Phage display screening can be performed under different conditions depending on the available functional format of the antigen. Solid-phase screening is the most commonly used method, where antigens are directly coated onto a solid surface. Alternatively, liquid-phase screening can be employed, where antigen expressing cells or biotinylated antigens bind to the phage in solution. Liquid-phase screening offers several advantages over solid-phase screening, including greater control over antigen concentration and the ability to avoid conformational changes in the antigen.
In liquid-phase screening, the phage-antigen complexes are captured, typically using streptavidin-coated beads if the antigen is biotinylated. The antigen-bound phage is then eluted through pH changes or protease digestion and reinfected into E. coli for amplification. After 3-4 rounds of selection, target-specific clones are obtained (Figure 1).
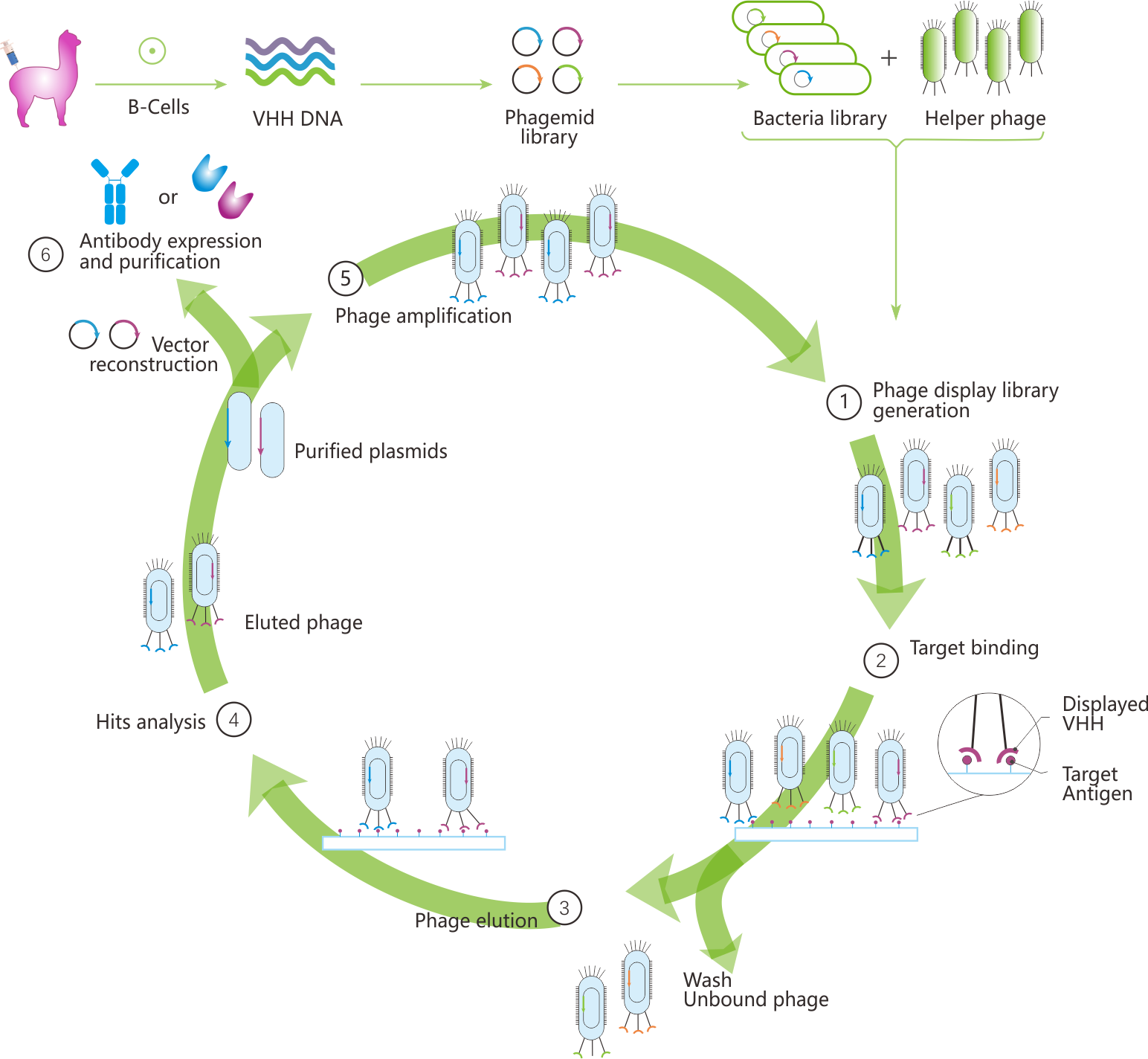
Fig 1. Workflow of phage display screening
Service Provided

Why chose our Phage Display system?
1. Large library size up to 10^9 CFUs.
2. Fast process and ease of development.
3. Absolutely background free cloning system.
4. Available for antigen presented on the surface of whole cells or tissue.

Tel:+86 4008677715
E-mail:service@nb-biolab.com
Address:SME Incubation Park, 319 Qingpi Avenue, Chengdu, China.
Working time:9:00-18:00