
- Home
-
Services
 Leading molecular discovery services
Leading molecular discovery services
 Antibody Discover Service
Antibody Discover Service
 Technology platform
Technology platform
 Technology optimization service
Technology optimization service
- Products
- Resources
- Publication
- Contact Us
Antigen Preparation and Camelids Animal Immunization
We offer high-quality, reliable animal immunization services backed by our well-regulated animal farms, extensive project expertise, and versatile immunization platforms. With a proven track record of success, we design tailored immunization strategies based on your target antigen’s unique characteristics, ensuring optimal immune responses while reducing risks and costs.
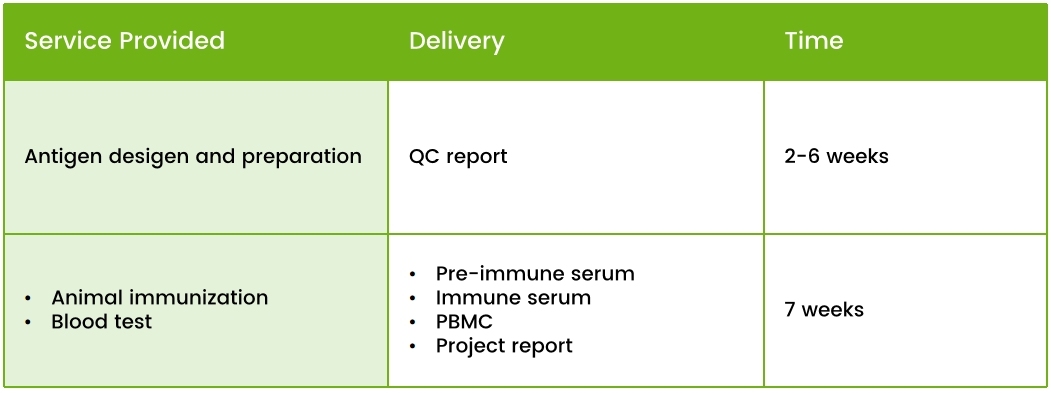
49-day Animal immunization
Animal immunization can involve various forms of antigens, such as LNP-mRNA, VLP proteins, recombinant proteins. The standard immunization protocol typically includes a total of 4 antigen injections, with a 2-week interval between each injection, and a total of 3 serum titer tests.
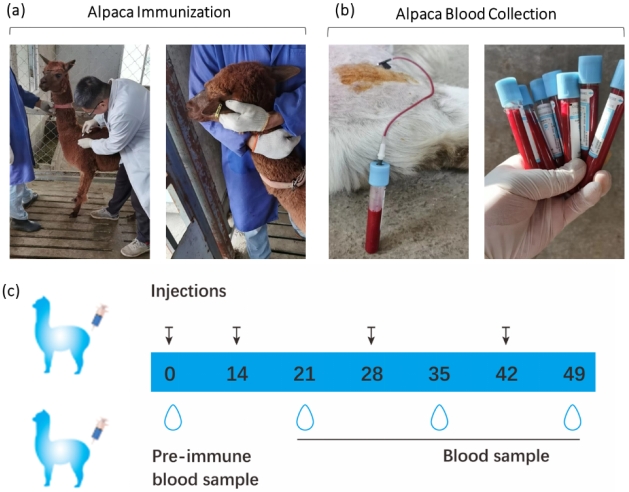
Figure 1. Animal immunization and blood collection. (a) Alpaca immunization. (b) Alpaca blood collection. (c) 49-day immunization timeline. Black arrows indicate antigen injection times, and droplet symbols represent blood sample collection. Samples collected on days 21, 35, and 49 are used for titer testing, with the day 0 sample serving as the negative control.
Diversified Immunization Platform
1. Immunization Animals: Camelids (Camel, Alpaca, Llama)
2. Adjuvants: Freund's adjuvant and water-soluble adjuvants
3. Injection Methods: Subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, intramuscular, nasal spray
4. Immunogen Formats: Soluble proteins, peptides, cells, VLP proteins, LNP-mRNA, and adenoviral expression vector DNA
Our Service Offerings
1. Customized Immunization Plans
2. Antigen Design and Preparation
3. Immunization with Naive Camelids
4. Blood sample collection and serum titer analysis by ELISA/FACS.
5. Isolation and preservation of animal PBMCs.
Distinct Features of Heavy-chain Antibodies (HcAbs) in Common Camelid Species
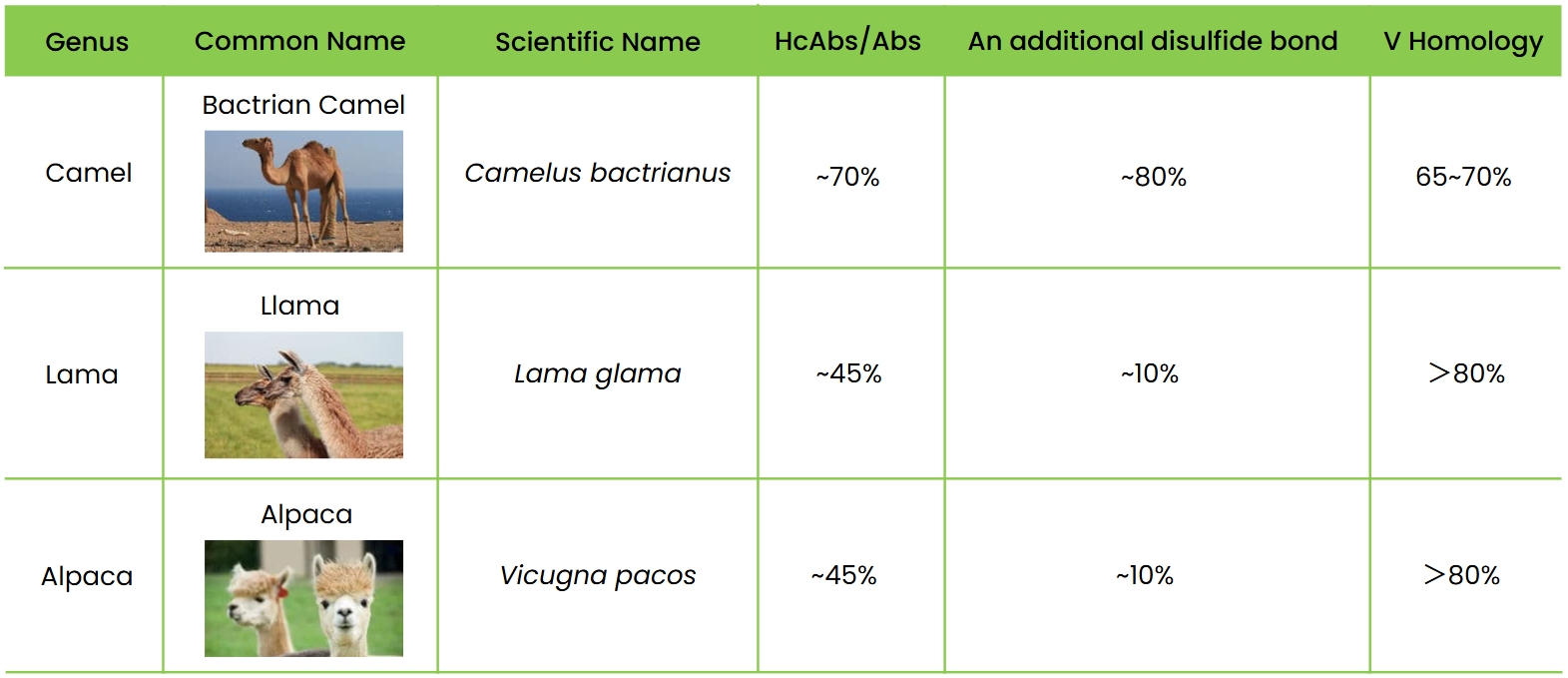
The Camelidae family consists of 3 genera and 6 species, with camels, alpacas, and llamas being the most common. Camels are the largest and most distinct, while alpacas (up to 60 kg) differ from llamas (127-204 kg) primarily in size and coat characteristics.
VHH antibodies typically form disulfide bonds at positions 23 and 104, with additional bonds often occurring between CDR1/FR2 and CDR3. These extra bonds stabilize the antibody but may cause mismatches during production, potentially leading to a loss of activity if mutated. While camelid serum contains high levels of single-domain antibodies (HcAbs), over 85% of camelid HcAb sequences feature two pairs of disulfide bonds, compared to only about 10% in alpaca and llama HcAbs.
Why choose us for your VHH discovery project?
1. Guaranteed Zero Background: We ensure that the animals used for immunization have no prior exposure to the target antigen, providing clean, unbiased results.
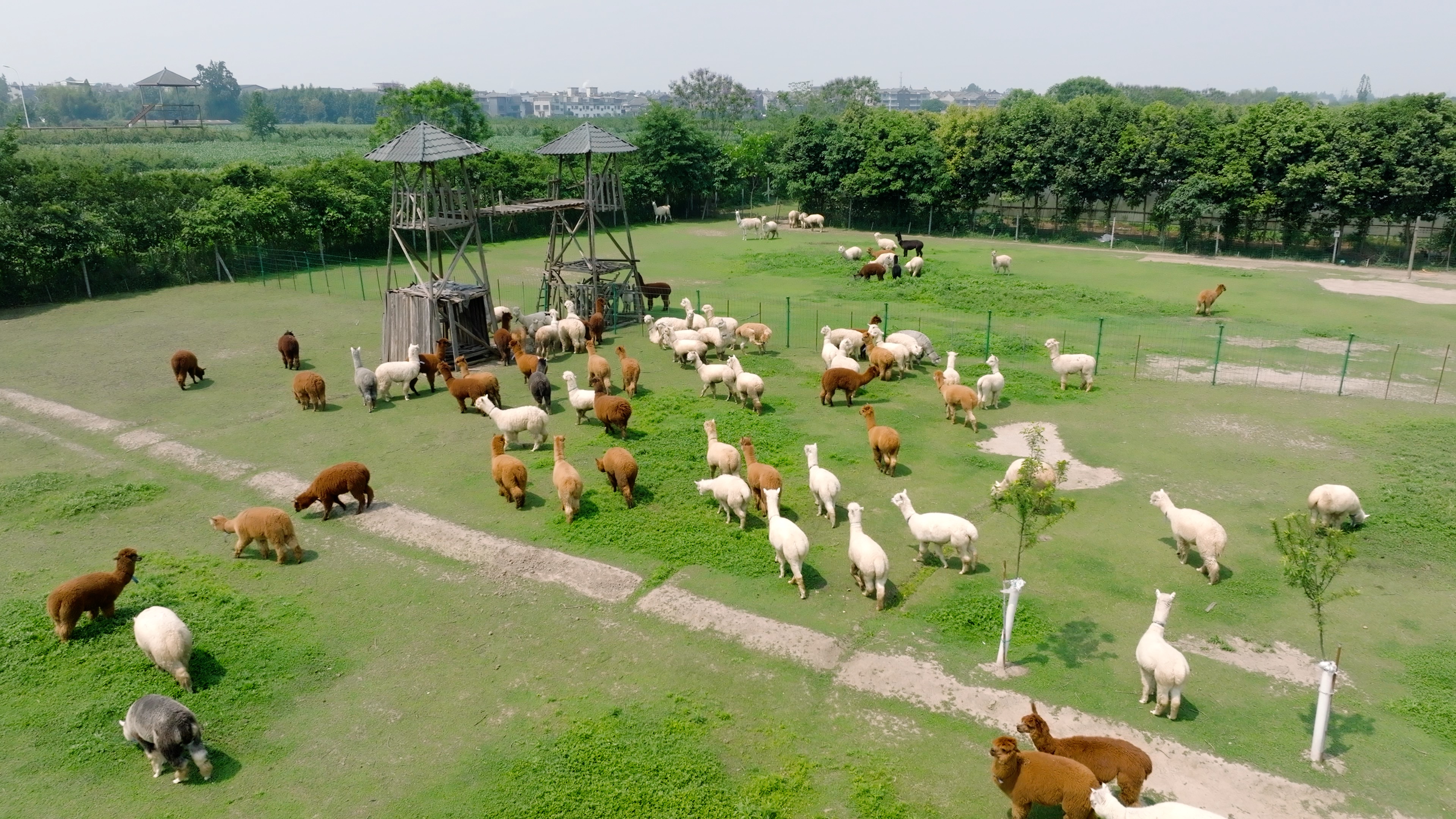

Figure 2. Our company-owned 40-acre farm, where we import top-tier alpacas and llamas from South America. With advanced facilities, expert breeders, and comprehensive veterinary care, we ensure the highest standards for animal health and IP protection.
2. Antigen Design Platform
Antigen Selection & Custom Design: We collaborate with you to identify and design the most suitable antigens tailored to your specific research objectives, ensuring the best possible results for your project.
Antigen Preparation & Optimization: Our services cover the preparation of VLPs, mRNA, fusion proteins, and other antigens, all of which are carefully optimized for improved stability, enhanced immune responses, and effectiveness in subsequent VHH screening.
3. Proprietary Camelid Immune Adjuvant: Induces strong immune responses, boosts HcAb titer, and preserves antigen conformation with low toxicity.
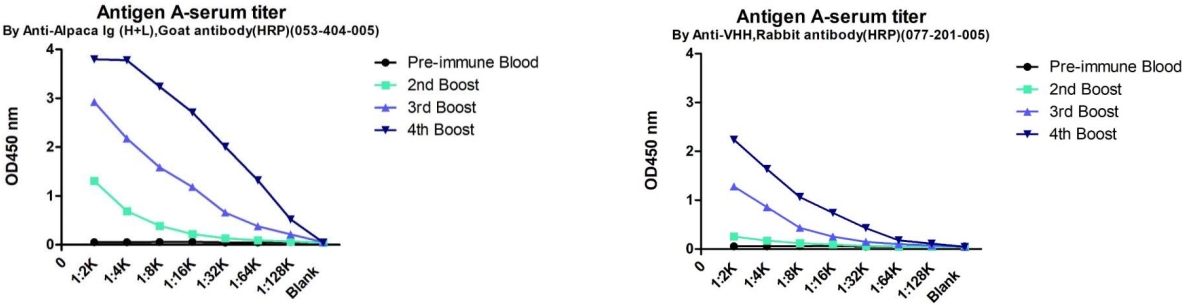
Figure 3. Serum titers following alpaca immunization with a Camelid Immune Adjuvant and antigen mixture. The left panel shows total IgG titers after four immunizations, while the right panel presents VHH titers. The X-axis represents serum dilution, and the Y-axis shows OD values measured by ELISA.
4.Proprietary serum titer detection antibody: Specifically designed for direct detection of single-domain antibody titers in serum.
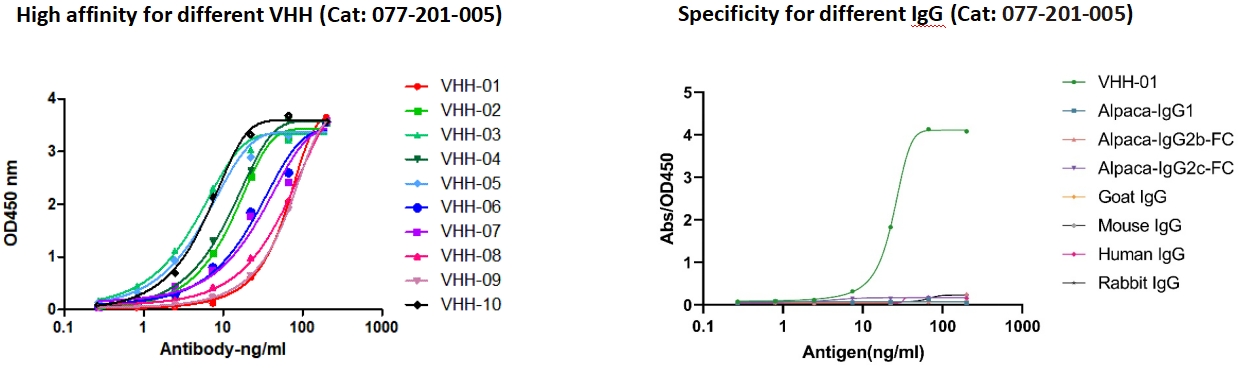
Figure 4. The left panel shows that AlpHcAbs (VHH detection antibody) exhibits stable, high-specificity, and sensitive recognition of all camelid-derived VHH sequences.The right panel confirms that AlpHcAbs specifically binds VHH conformations, without reacting with other alpaca or cross-species antibodies.