- Home
-
Services
 Leading molecular discovery services
Leading molecular discovery services
 Antibody Discover Service
Antibody Discover Service
 Technology platform
Technology platform
 Technology optimization service
Technology optimization service
- Products
- Resources
- Publication
- Contact Us
Oral, injections, inhalation (medication for asthma), topical medication and nasal drops are the five generally drug delivery methods.
So How long for a drug to be eliminated from the body after entering it? Here comes the concept of half-life. The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body, and it helps determine dosing interval and duration of therapy.
Conventional antibodies exhibit longer half-lives due to their larger molecular weight and specific binding to the Fc receptor, FcRn, which prevents lysosomal degradation. The antibody-FcRn complex then transports to the cell membrane surface where it dissociates and is released back into the plasma, resulting in a prolonged half-life[1].
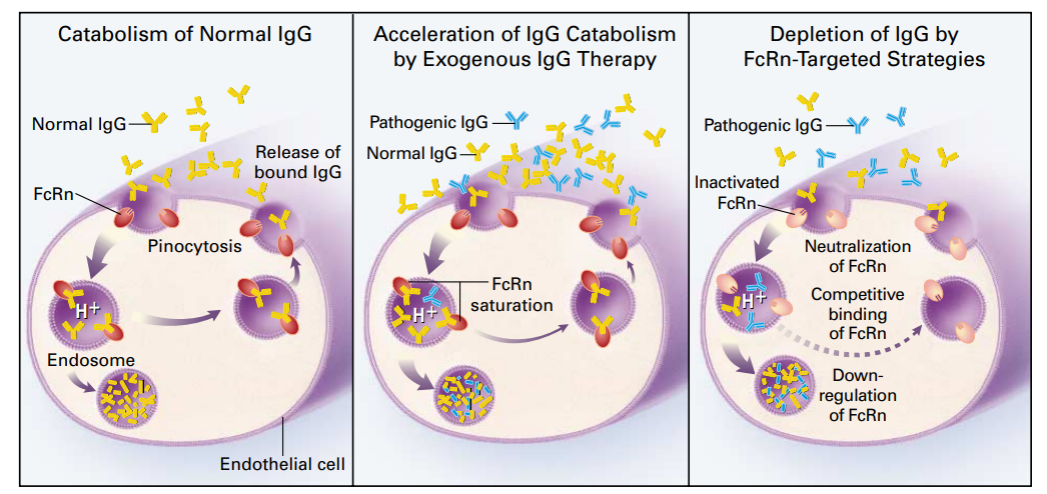
Figure 1. Regulatory mechanism of IgG metabolism by FcRn
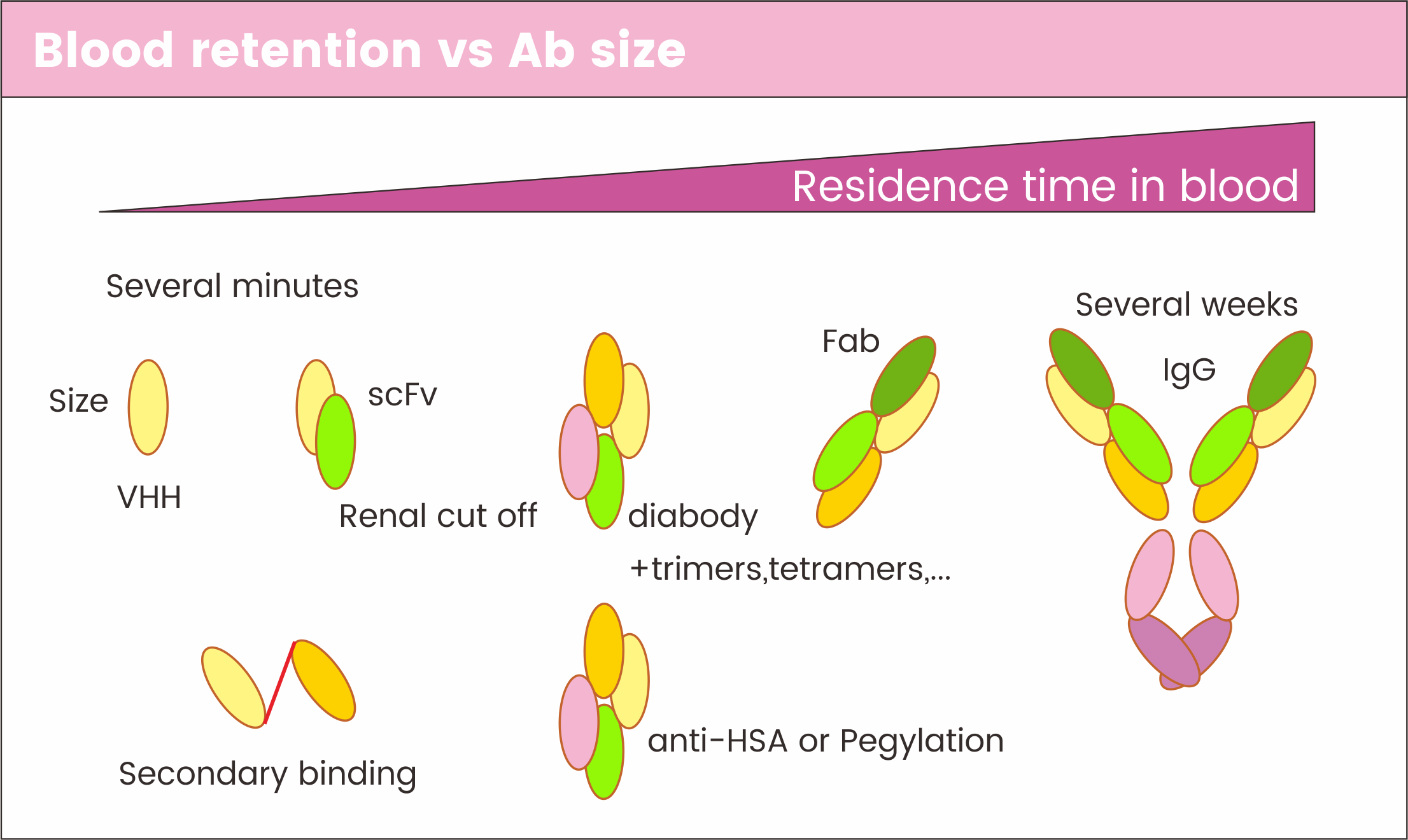
Nanobodies, with their molecular weight of 15 kDa, have a short half-life of a few minutes due to their small size, resulting in rapid clearance by glomerular filtration. Despite their promising applications in disease diagnosis and treatment, the small size of nanobodies and other antibody fragments, such as scFv (28 kDa) and Fab (50 kDa), limits their therapeutic efficacy as they are cleared by the body's filtration System. Hence, enhancing the half-life of nanobodies is an improtant task for their in vivo use.
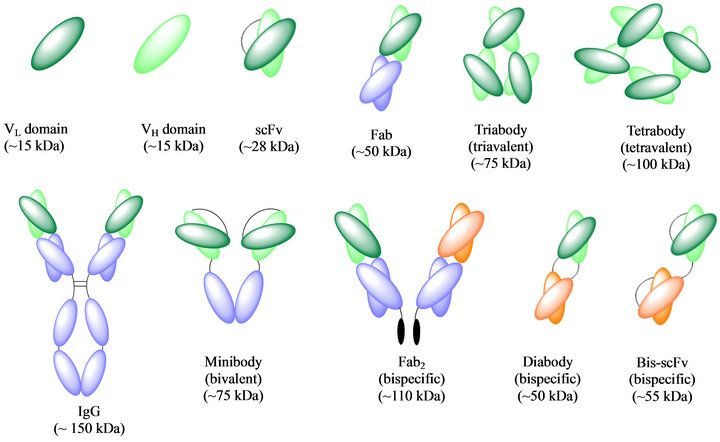
Figure 2. Structure and molecular weight of different forms of antibodies
Common methods used to extend nanobody half-life include coupling polyethylene glycol (PEG) to increase molecular weight, forming fusion proteins by attaching nanobodies to the Fc region of antibodies, binding nanobodies to human serum albumin (HSA) using tandem anti-HSA nanobodies, and creating multivalent and multispecific nanobodies through tandem association. Nanobody drugs currently marketed and under development typically employ fusion with Fc or HSA to address the short half-life issue, which will be further discussed regarding their principles and efficacy.
Nanobody binds to HSA
1. Characteristics of HSA
HSA is a cardioid molecule composed of 585 amino acids, arranged primarily in α-helix structures and divided into three homology domains (DI, DII, and DIII) with subdomains A and B (DIA, DIB, DIIA, DIIB, DIIIA, and DIIIB) connected by flexible loops, as revealed by its X-ray crystal structure [3]
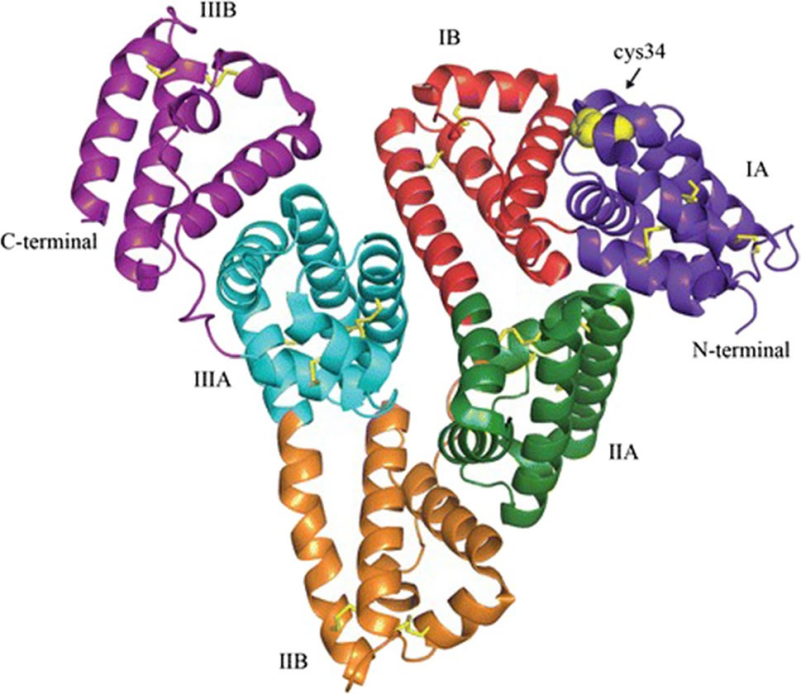
Figure 3. 3D structure of albumin
HSA, the most abundant and structurally stable protein in human plasma, has a concentration of approximately 45 mg/ml (0.6 mM) and a circulating half-life of up to 20 days. Nanobod binds to HSA increasing its hydrodynamic radius and molecular weight increase, leading to decreased glomerular filtration and prolonged retention time in vivo. Additionally, FcRn-mediated recirculation prolongs the half-life of nanoantibodies from hours to over 3 weeks.
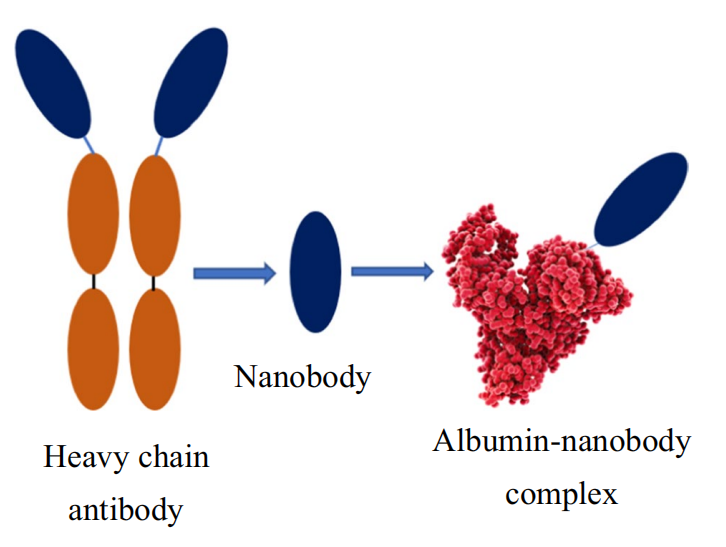
Figure 4. Schematic diagram of the albumin-nanobody non-covalent binding complex
2. Example
Anti-HSA VHHs can enhance drug half-life by binding drugs to HSA. Bispecific nanobodies that target tumor antigens, CD16, and HSA have been developed, including Ozoralizumab, a humanized, trivalent bispecific nanobody developed by Ablynx, was approved in Japan in September 2022 (Nanozora®),making it the world's first approved bispecific nanobody. Ozoralizumab contains three nanobody domains, two targeting TNF-α and one binding to HSA, resulting in a mean half-life of 18.2 days after a single dose.

Figure 5. Schematic diagram of the structure of Ozoralizumab
Nano-antibody coupled with antibody Fc fragment
1. Structure and function of antibody Fc fragment
The antibody Fc fragment is a constant region of the antibody consisting of a specific sequence of amino acids that is shared among different antibodies. The structure of the antibody Fc fragment determines the various types of antibodies. Unlike monoclonal antibodies, nanobodies lack the Fc fragment, which results in a shorter half-life and the absence of Fc-mediated effector functions, such as antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxic (ADCC) effects and serum stability. ADCC effects are mainly mediated by natural killer (NK) cells, and the Fc receptor FcγRIIIa (CD16a) on their cell surface plays a crucial role in recognizing and binding to the Fc fragment.
2. Example
Nanobodies can easily couple Fc fragments to reconstitute humanized heavy chain antibody forms to achieve including Fc-mediated effector functions and increase blood retention time, but will also inevitably reduce their diffusion advantage. The choice of Fc fusion fragments, with a preference for IgG1 Fc, is related to the affinity binding properties of IgG1 to the Fc receptor protein.
The most successful nano-antibody drug using Fc fusion technology is Envida® (KN035) from Alphamab Oncology. It is the world's first approved subcutaneously administered PD-(L)1 antibody for the treatment of adult patients with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability (MSI-H) or mismatch repair gene-deficient (dMMR) advanced solid tumors [9]. KN035's PD-L1 binding molecule contains immunoglobulin Fc region allows the formation of dimers and prolongs the in vivo half-life of molecule by approximately 200 hours.
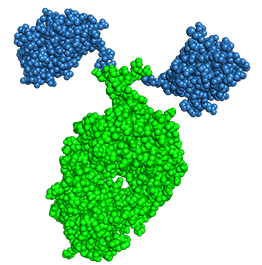
Figure 7. Crystal structure of KN035
Some of these methods have already been approved for clinical use or are currently being tested in clinical trials. With the emergence of more effective techniques, it is anticipated that more nanobody-based drugs will be developed, advancing the progress of human health.
References
[1].Yu Z, Lennon V A. Mechanism of Intravenous Immune Globulin Therapy in Antibody-Mediated Autoimmune Diseases[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine, 1999, 340(3): 227-228.
[2] Divsalar, A. et al. Characterization and side effect analysis of a newly designed nanoemulsion
Targeting human serum albumin for drug delivery. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2012. 98: p. 80-84.
[3] Lamichhane S, Lee S. Albumin nanoscience: homing nanotechnology enabling targeted drug delivery and therapy. Arch Pharm Res. 2020;43(1):118-133. doi:10.1007/s12272-020-01204-7
[4] Heukers, R., et al., Targeting hepatocyte growth factor receptor (Met) positive tumor cells using internalizing nanobody-decorated albumin nanoparticles. biomaterials, 2014. 35(1): p. 601-610.
[5] Altintas, I., R.J. Kok, and R.M. Schiffelers, Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor in tumors: from conventional monoclonal antibodies via European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2012. 45(4): p. 399-407.
[6] Roovers, R.C., et al., A biparatopic anti-EGFR nanobody efficiently inhibits solid tumour growth. international journal of cancer, 2011. 129(8): p . 2013-2024.
[7] Hoefman, S., et al., Pre-clinical intravenous serum pharmacokinetics of albumin binding and non half-life extended Nanobodies®. Antibodies, 2015. 4(3): p. 141-156.
[8] Elsadek, B. and F. Kratz, Impact of albumin on drug delivery-new applications on the horizon. journal of controlled release, 2012. 157( Journal of controlled release, 2012. 157(1): p. 4-28.
[9] Fei Zhang., et al., Structural basis of a novel PD-L1 nanobody for immunecheckpoint blockade ,Cell Discovery 3(2017)