Conventional lgG1 antibody
Monoclonal antibodies have many applications as research tools and, increasingly as therapeutic or diagnostic agents. Dozens of diferent monoclonal antibodies have received regulatory approval to treat a varity of ditferent diseases. Engineering monoclondl antibodies are necessary for the utility of rodent (specifically murine) monoclonal antibodiesin human therapy because of problems asociated with their non-human origin, in particular, their immunogenicity in a human host.
Camelidae produce functional antibodies that do not incorporate light chains, classified as IgG2 and IgG3. In addition to these isotypes, Camelidae also produce conventional antibodies (IgG1), which are an attractive starting point for engineering monoclonal antibodies with potential utility as human therapeutics.
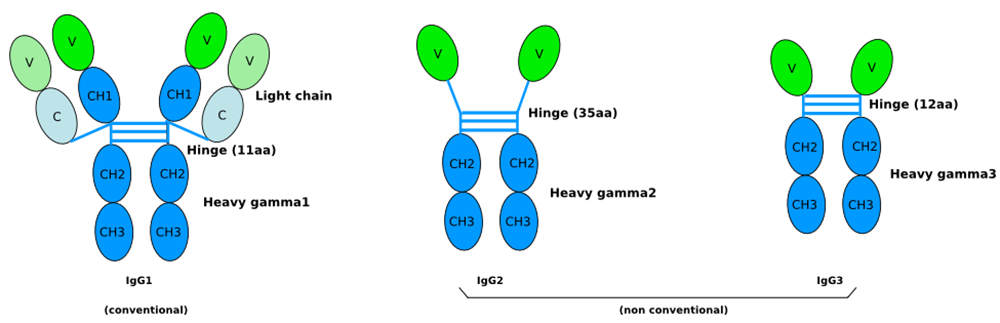
Advantages of conventional antibodies from the family camelidae
Phylogenetic Distant Relationship with Humans Enables High Specificity Antibodies
Species in the family Camelidae are phylogenetically quite distant from humans, which enables the production of antibodies with high specificity and affinity against a broad range of therapeutic target antigens, particularly when the target antigen has high homology with rodents or when an in vivo assay using a mouse model is involved for antibody validation.
Outbred Camels Produce Strong and Diverse Antibody Responses
Unlike highly inbred mouse strains, an outbred camelid animal has beneficial consequences for the strength and diversity of the antibody response.
High Structural Homology in Camelid and Human Antibodies
The hypervariable loops of camelid variable heavy (VH) and variable light (VL) domains often exhibit a high degree of structural homology with the hypervariable loops of human VH and VL domains. Conventional camelid VH and VL domains exhibit a remarkably high sequence homology to their human counterparts over the framework regions. In fact, the degree of sequence identity between camelid conventional variable domains and human variable domains can approach that observed between humans and other primate species, such as cynomolgus monkeys.
Few Mutations Required for Humanization of Camelid Antibodies
The high percentage of structural and sequence homology between camelid conventional antibodies and human antibodies means that only a small number of mutations are required for humanization compared to rodent monoclonal antibodies, which require a complex and time-consuming procedure. The consequent benefit is maintaining maximum affinity and potency from the mother clone.
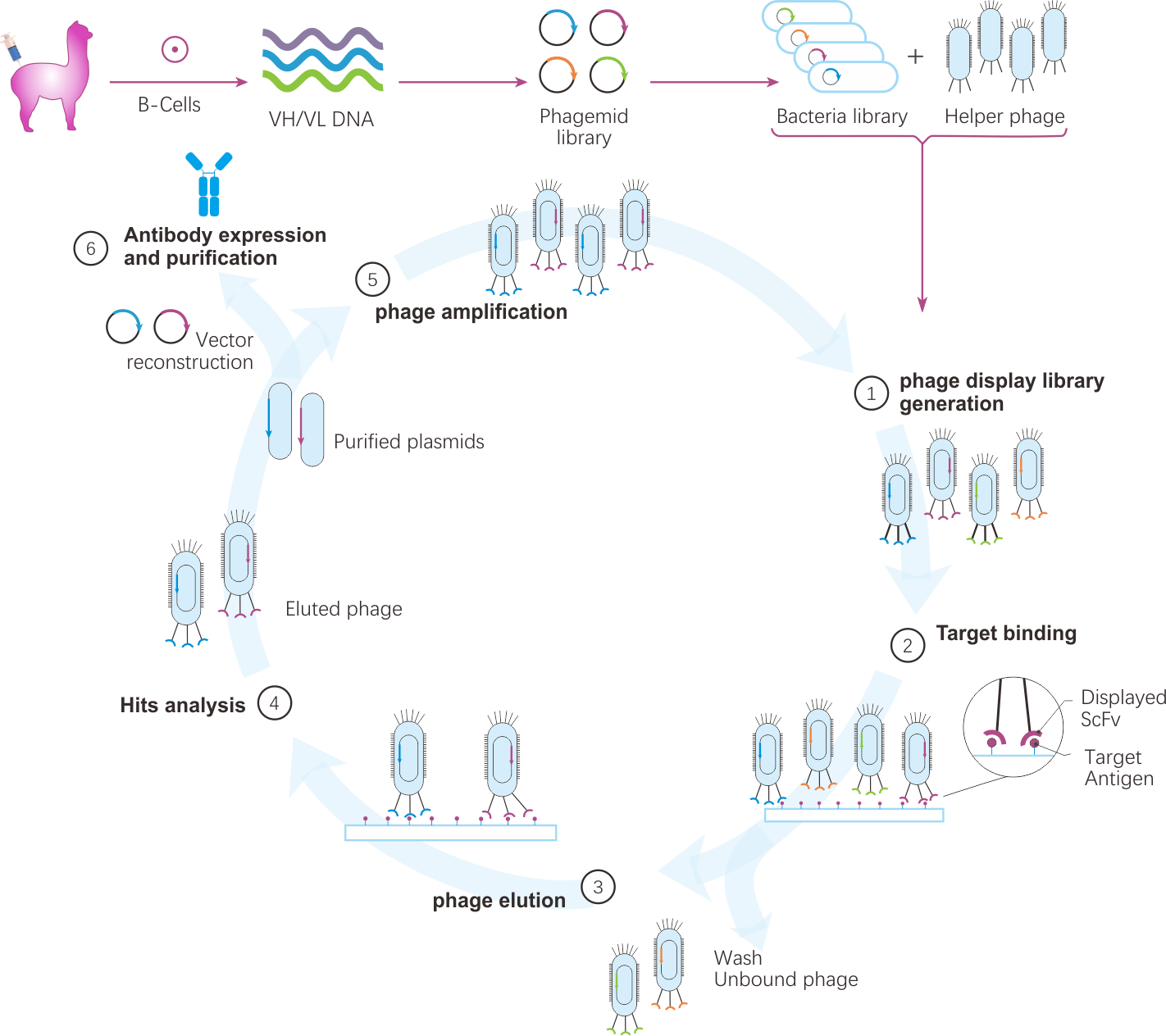
Workflow of monoclonal antibodies discovery on phage dispaly platform
The unique properties of camelid IgG1 antibodies make them an attractive alternative to conventional antibodies. Unlock the full potential of camelid IgG1 antibody with our well established antibody discovery platform.