Single domain antibodies (sdAbs) have gained increasing popularity in antibody drugs and cell therapy, prompting many researchers to engage in sdAb development. From literature, three animals commonly used for this purpose are camels, alpacas, and llamas, which belong to the Camelidae family. This family has only three genera and six species, distributed across Asia and Africa (tribe Camelini) and South America (tribe Lamini). The camel tribe, with a large body and humps adapted to desert life, includes two to three species: dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius), Bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus), and wild camel (Camelus ferus). The llama tribe, with a smaller body and no humps, is descended from a group that entered South America from North America, and includes the domesticated llama (Lama glama) and alpaca (Lama pacos) with rich color varieties.
Appearance features
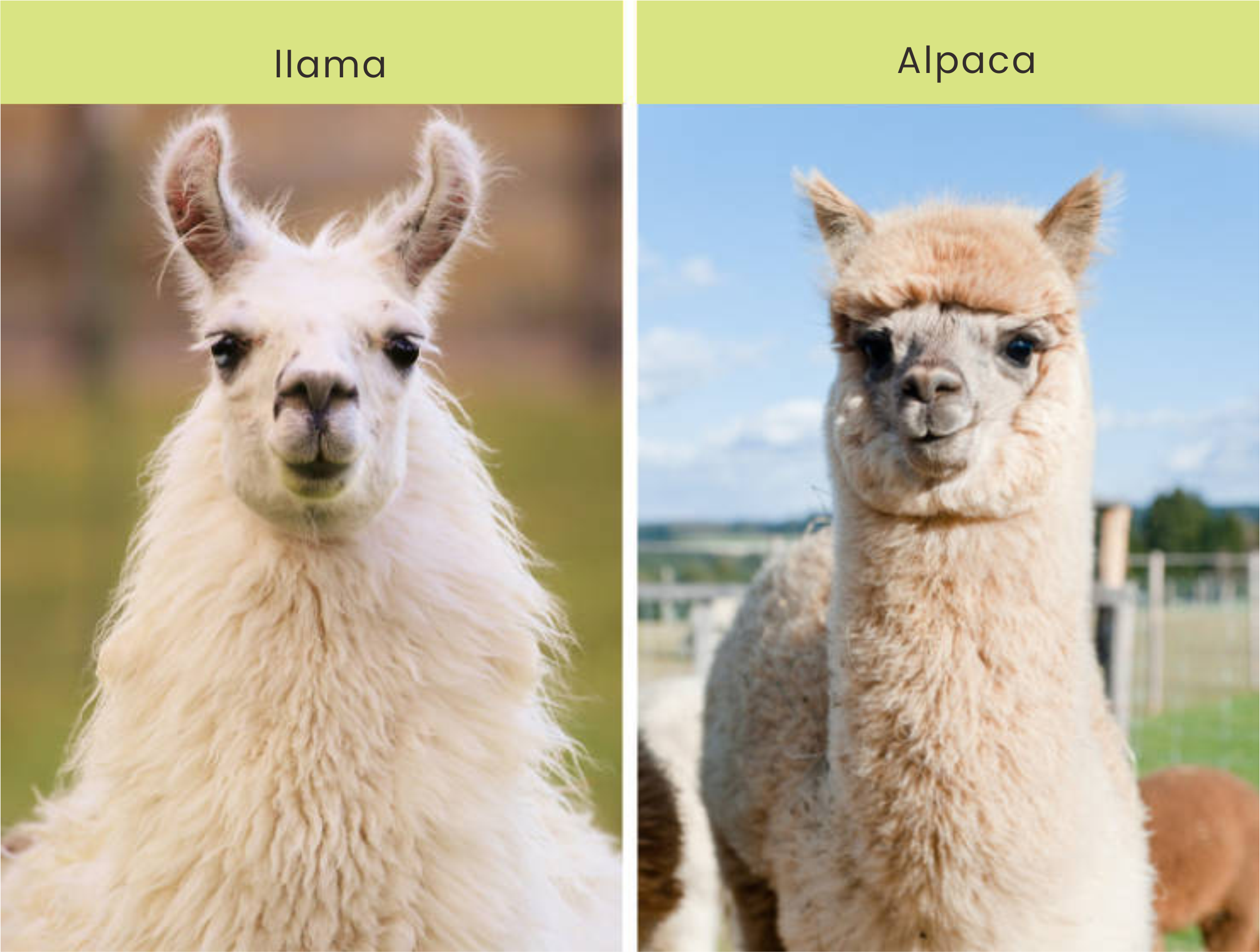
Camels are the most easily distinguishable, while the main difference between alpacas and llamas lies in body size. Alpacas generally weigh around 60 kg when fully grown, while llamas can reach 127-204 kg. Llamas have less leg hair, large and curved banana-shaped ears, and shorter hair on their face. Alpacas have thicker leg hair, large and erect ears that are short in length, and thicker hair on their face that matches their body.

Single-domain antibody content in the three animals
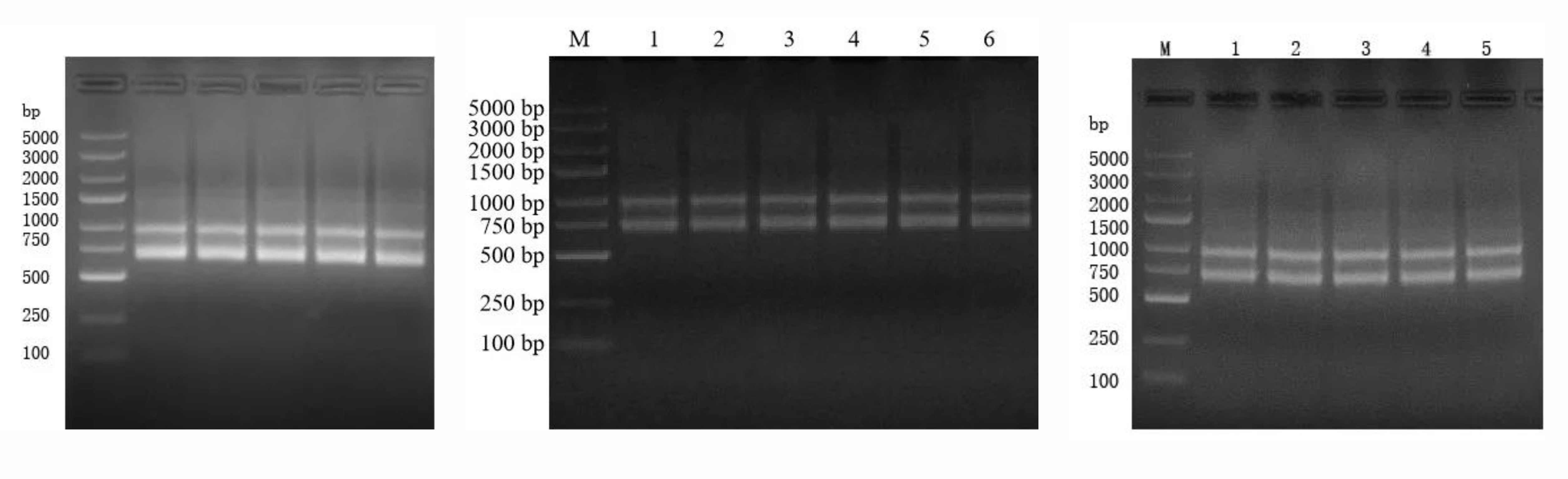
Regarding the single-domain antibody content in these animals, camels exhibit the highest levels, approximately 70%, whereas alpacas and llamas exhibit a range between 25% and 45%. This is further supported by the PCR amplification of VHH fragments, which suggests that camels are more suitable for screening sdAbs due to their higher content of single-domain antibodies.
Germline data of single-domain heavy chain antibodies from the IMGT database
Camel
http://www.imgt.org/IMGTrepertoire/index.php?section=LocusGenes&repertoire=genetable&species=arabian_camel&group=IGHV
We can identify that the conventional tetrameric IgG1 of Camel consists of IGHV3S1 to IGHV3S41. In contrast, IGHV3S42 to IGHV3S74 comprises a total of 33 germline genes for heavy chain only antibodies.
Alpaca
http://www.imgt.org/IMGTrepertoire/index.php?section=LocusGenes&repertoire=genetable&species=Vicugna_pacos&group=IGHV
IGHV3-3 and IGHV3S53 to IGHV3S68 are 17 germline genes for heavy chain only antibodies.
Llama
http://www.imgt.org/IMGTrepertoire/index.php?section=LocusGenes&repertoire=genetable&species=Llama&group=IGHV
IGHV3S1 to IGHV3S5 are 5 germline genes for heavy chain only antibodies.
Location and abundance of intramolecular disulfide bonds
Intramolecular disulfide bonds are commonly formed between residues 23 and 104 in VHH antibodies, and may also occur between CDR1 or FR2 and CDR3, playing a crucial role in stabilizing the antibody structure. The presence and number of these bonds are species-specific, and can vary significantly between camels, alpacas, and llamas.
Despite their importance for antibody stability, intramolecular disulfide bonds are susceptible to mispairing during the manufacturing process, and any mutations affecting their formation can lead to a loss of antibodyactivity. Therefore, understanding the precise location and abundance of these bonds is critical for optimizing the production and efficacy of VHH antibodies.
In earlier discussions about Camel, it was mentioned that the serum of Camel contains high levels of single-domain antibodies and that the germline of Camel antibodies is more diverse. However, except for IGHV3S42, the remaining 32 contain additional disulfide bonds. Among them, the disulfide bonds of IGHV3S43-IGHV3S71 are located in CDR1-CDR3, and the disulfide bonds of IGHV3S72-IGHV3S474 are located in the 50th amino acid of FR2 to CDR3. Through NGS analysis of NBbiolab's Phage & Yeast display based Naïve VHH libraries from Camelus bactrianus, it was found that over 85% of the sequences contain two pairs of disulfide bonds.
Among the 17 germline sequences of alpaca, 8 contain two pairs of disulfide bonds, with the additional disulfide bond located between position 55 and CDR3. By analyzing NBbiolab's phage display-based naive VHH libraries from alpaca using NGS, it was found that 32% of the sequences contain two pairs of disulfide bonds.
In llama, among the 5 germline sequences, 3 have two pairs of disulfide bonds, with the additional disulfide bond located between position 55 and CDR3. By analyzing NBbiolab's phage display-based naive VHH libraries from llama using NGS, it was found that 22.3% of the sequences contain two pairs of disulfide bonds, which is consistent with the literature reporting that llamas have the lowest number of disulfide bonds among these three species in their serum.
The homology of sdAbs with human VH
The homology between camel VHH and human VH ranges from 67.5% to 74.3%, while the homology between alpaca, llama, and human VH ranges from 80% to 87.3%.